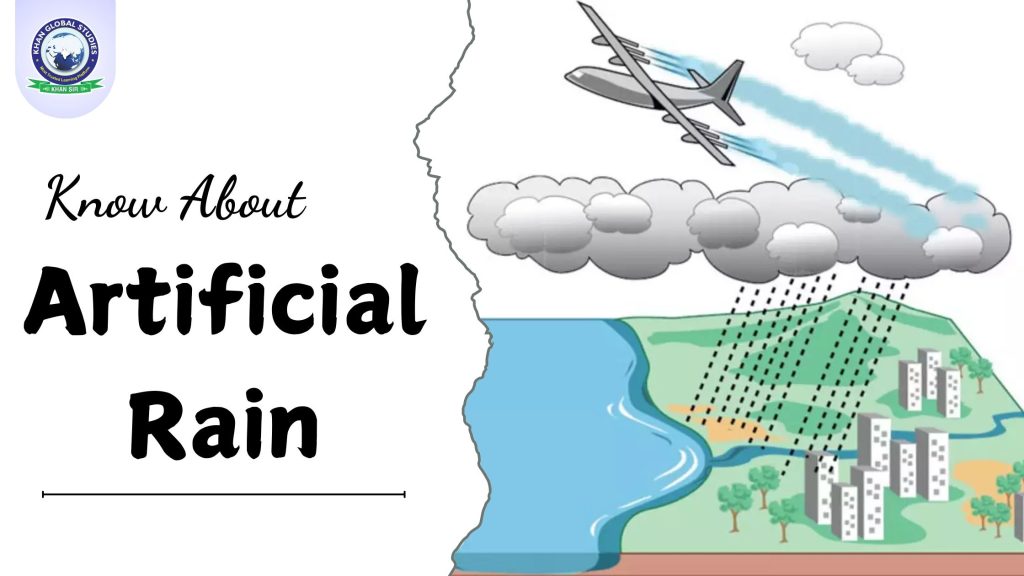
Artificial rain, also known as cloud seeding, is a process in which scientists attempt to artificially induce rain by dispersing specific chemicals into clouds. This weather modification technique is widely used in areas that are drought-prone or where natural rain is scarce. Using substances such as silver iodide, sodium chloride or dry ice, cloud seeding promotes condensation within clouds, increasing the likelihood of rain.
How Cloud Seeding Works?
The main purpose of cloud seeding is to promote rain in arid areas and reduce hail damage or even clear fog. Scientists use two main types of seeding:
- Static cloud seeding: This technique involves injecting ice-nucleating agents such as silver iodide into cold clouds to stimulate the formation of ice crystals. These ice crystals eventually grow large enough to fall as rain.
- Dynamic cloud seeding: This method thickens clouds and increases their moisture content by increasing vertical air currents, leading to more rain.
Cloud-seeding material is usually dispersed via airplanes, ground-based generators, or drones equipped with special equipment. Emerging methods, including electric charge and laser technology, are also being researched to improve seeding efficiency.
Historical Background of Cloud Seeding
The idea of manipulating the weather goes back to 1891 when Louis Gathmann proposed creating rain by adding liquid carbon dioxide to clouds. It was not until 1946 that Vincent Schaeffer successfully demonstrated the first effective cloud seeding using dry ice. His experiment resulted in snowfall in Massachusetts, setting a precedent for future weather modification initiatives.
Further progress was made in the 1960s when cloud seeding was used to weaken storms, most notably under Project Stormfury, which aimed to reduce the intensity of storms.
Modern Cloud Seeding Techniques
Today, cloud seeding has evolved into a more sophisticated technique, with several techniques used globally:
- Silver iodide: The most common substance used in cloud seeding due to its structural similarity to ice crystals. It is particularly effective in cold clouds.
- Hygroscopic seeding: This method is used in warm clouds, where substances such as table salt are dispersed to encourage the aggregation of water droplets, promoting rain.
- Electric charge: The UAE pioneered the use of drones that emit electric charges to manipulate water droplets in the atmosphere, causing rainfall. This approach saw success in 2021 when it rained in Al Ain.
- Infrared laser pulse: In 2010, researchers in Berlin tested infrared laser pulses to create condensation nuclei in the atmosphere. The concept involves creating particles from sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide, which serve as seeds for the formation of raindrops.
Effectiveness of Cloud Seeding
Despite its potential, the effectiveness of cloud seeding remains a subject of debate among scientists. Some studies suggest that the effect of cloud seeding on rain levels is limited or uncertain. For example, the Wyoming Weather Modification Pilot Program estimated a modest 3% increase in snowfall across the season, while the National Research Council stated in 2003 that there was no definitive evidence of its effectiveness.
However, modern advancements and new technologies have shown promising results. Jeff Tilly of the Desert Research Institute commented in 2016 that cloud seeding has become a reliable and cost-effective method for water supply management.
Difference Between Natural and Artificial Rain
| Natural Rain | Artificial Rain |
| Natural rainfall occurs naturally through the process of condensation and precipitation in clouds. | Artificial rain attempts to cause condensation and rainfall in clouds by spraying chemicals. |
| It completely depends on natural processes. | It can be controlled by human intervention. |
| It depends on weather and climatic conditions. | It is possible only when sufficient amount of clouds are present. |
| There is no additional cost involved in natural process. | Artificial rain requires high cost and technical equipment. |
Applications of Cloud Seeding
Cloud seeding serves many purposes around the world, especially in areas where water resources are critically low or where specific weather conditions are needed for agricultural, environmental, or social purposes.
Agricultural Support
Cloud seeding is often used to mitigate droughts, helping farmers maintain adequate water supplies for their crops. By increasing rainfall during critical periods, this technique provides a lifeline for agriculture in arid regions.
Water Supply Augmentation
Countries such as China, India, and the United States use cloud seeding to increase water reserves. In areas where natural rainfall is insufficient, cloud seeding helps replenish lakes, rivers, and reservoirs, ensuring the availability of water for human consumption and agriculture.
Disaster Management
Cloud seeding can help control forest fires by inducing rain in affected areas. It can also reduce the effects of air pollution by bringing harmful particles to the ground, improving air quality.
Weather Control for Events
Cloud seeding has been used to ensure favourable weather during large events. For example, during the 2008 Beijing Olympics, China used cloud seeding to prevent rain from disrupting outdoor events.
Environmental and Health Concerns
One of the primary concerns associated with cloud seeding is the potential environmental impact of the chemicals used. Although silver iodide is the most common agent and is considered relatively safe, there are concerns about its long-term accumulation in the environment and its impact on human health.
Additionally, cloud seeding can have unintended consequences on natural water cycles. By artificially increasing rainfall in one area, there is a risk that it could disrupt weather patterns elsewhere, potentially causing drought or flooding in neighbouring areas.
Challenges and Limitations
Cloud seeding, despite being a promising technology, has its limitations:
- Cost: The process involves a substantial financial investment in aircraft, chemicals, and monitoring equipment.
- Dependence on cloud conditions: Cloud seeding is only effective when atmospheric conditions are favourable, meaning that clouds with sufficient moisture must be present for seeding to work.
- Ethical and legal issues: The use of cloud seeding for military purposes is prohibited under international law, following concerns raised during the Vietnam War, where cloud seeding was used to extend the monsoon season in Operation Popeye.
Cloud Seeding in India
India has also adopted cloud seeding as a measure to tackle water scarcity, particularly in states such as Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. Over the past few years, these states have launched cloud seeding campaigns to improve agriculture and drinking water availability.
In 2017, Maharashtra launched a large-scale cloud seeding program during a prolonged drought. Airplanes were used to disperse silver iodide into clouds, leading to successful rainfall in critical areas. The state continues to explore cloud seeding as part of its comprehensive water management strategy.
The Future of Cloud Seeding
As global demand for water increases and climate change exacerbates drought conditions, cloud seeding could play an important role in managing water resources. Innovations in drone technology, the use of lasers and electric charge methods offer new possibilities for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of cloud seeding.
However, continued research and careful management are necessary to ensure that cloud seeding is done in an environmentally responsible manner, minimising potential negative impacts and maximising its benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is artificial rainfall?
Answer: Artificial rainfall is a scientific process in which chemicals are sprayed into clouds to artificially induce rainfall. This is also known as “cloud seeding”.
Q2: How is artificial rainfall created?
Answer: Artificial rainfall is created by releasing chemicals such as silver iodide, dry ice or sodium chloride into clouds using aeroplanes, rockets or drones. These chemicals help condense water vapour in the clouds and form rainfall.
Q3: What is the difference between natural rainfall and artificial rainfall?
Answer: Natural rainfall occurs through natural processes, while artificial rainfall is created by humans by spraying chemicals into the clouds. There is no cost associated with natural rainfall, but artificial rainfall requires special technology and equipment.
Q 4: Where is artificial rainfall used?
Answer: Artificial rainfall is used in many areas, including:
- Drought-affected areas: To save crops and overcome water shortages.
- Sports events: To prevent rain and ensure clear weather.
- Environmental disasters: To extinguish forest fires and reduce air pollution.
- Water management: To fill reservoirs and lakes.
Q 5: What is the success rate of artificial rainfall?
Answer: The success of artificial rainfall depends on the condition of clouds and the weather. It works only when enough clouds are present. Its success rate can range from 30% to 70%.
Q 6: Are there any drawbacks to artificial rainfall?
Answer: Yes, there are some drawbacks:
- High cost: The process is expensive.
- Environmental impact: Chemicals such as silver iodide can have long-term negative effects on the environment and human health.
- Effect on natural water cycle: Artificial rainfall can disrupt the natural water cycle, potentially leading to drought or flooding in other areas.
Q 7: In which states of India has artificial rainfall been used?
Answer: Artificial rainfall has been used in states such as Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan to provide drought relief and manage water resources.
Q 8: Can artificial rainfall prevent climate change?
Answer: No, artificial rainfall is only a short-term solution. Long-term and comprehensive measures are needed to address climate change.
Q 9: What is the future of artificial rainfall?
Answer: Given the problems of increasing water scarcity and drought, the future of artificial rainfall looks promising. This technology can play an important role in managing water resources and addressing environmental challenges.
Q 10: Can artificial rain reduce air pollution?
Answer: Yes, artificial rain can help improve air quality by bringing harmful particles present in the atmosphere to the ground through rain, thereby reducing air pollution.