A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy are transferred from one organism to another through consumption. One way to show how living things are related to each other in an ecosystem is based on what they eat.
What is a Food Chain?
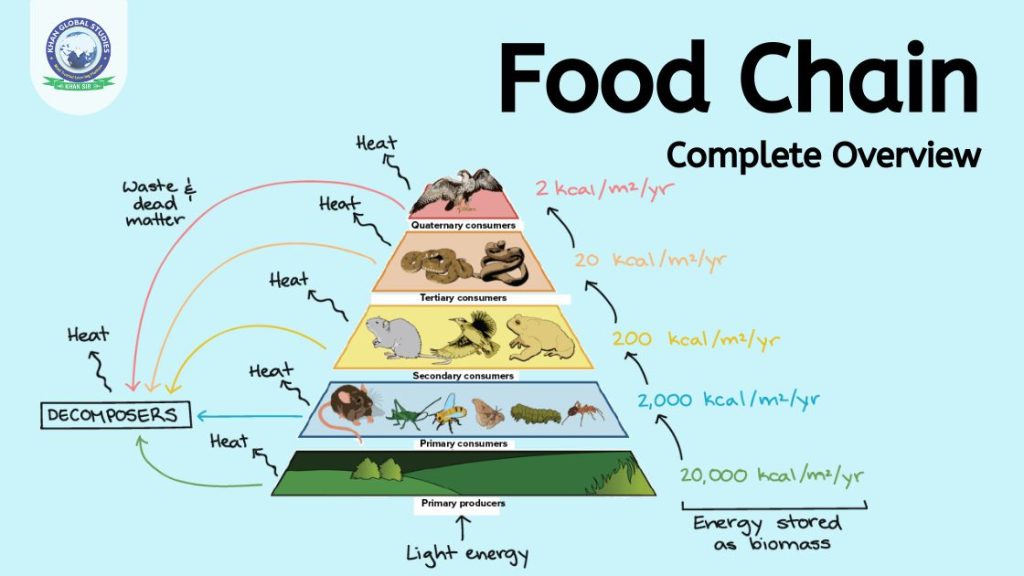
A food chain is a simplified model of the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem, which tells you about the food relationships between different organisms. Every organism lives at a specific trophic level, depending on what it eats. Producers, such as plants, live at the first trophic level, while herbivores, carnivores, and other organisms live at higher trophic levels. Energy and nutrients flow in one direction from lower to higher trophic levels, with only 10% of the energy available at one trophic level being transferred to the next trophic level.
Food Web and Examples
Now that you are familiar with what a food chain is, let’s understand the food web. The complex organization of organisms in ecosystems results in interconnected food chains. Whenever enough chains are joined together, they form a food web. The food web always represents the flow of energy as well as the energy consumed on a wide scale by any organism in the ecosystem. Often, multiple predators eat the same organism or multiple organisms are eaten by the same animal. In this state, it is unable to show accurate energy flow. Because many energy levels are interconnected. In this case, a food web would be a better solution to explain the flow of energy.
Types of Food Chains
There are two types of food chains known as the detritus food chain and the grazing food chain. Let us see these in detail-
Detritus Food Chain
The detritus food chain is a type of food chain that starts with dead organic matter, such as plant and animal remains, rather than living organisms. Detritus is broken down into smaller organic compounds by decomposers such as bacteria, fungi and other microorganisms, which are then eaten by other small organisms such as worms, snails and viruses. These viruses are then eaten by larger organisms such as crustaceans, insects and fish, which are in turn eaten by larger predators such as birds and mammals. The detritus food chain plays an important role in recycling nutrients and energy in ecosystems, as it converts dead organic matter into forms that living organisms can use.
Grazing Food Chain
It starts with autotrophs which include green plants, then moves towards herbivory and then carnivory. In this, energy is obtained from photosynthesis in the lowest trophic level. There are two types of rural food chains. The first is a predatory chain where one animal eats another animal. The animal that eats is called prey and the animal that eats is called predator. Secondly, it is the plants and animals in the grazing food chain that are infected by parasites.
What is the food chain in the terrestrial ecosystem?
The most important source of energy is the Sun and plants or producers use sunlight to make their food through the process of photosynthesis. The next element is the animal or consumer whose food is the plant at the previous level. The consumer neither produces food nor consumes energy, but receives the energy produced by plants in the form of food. Furthermore, the organisms that consume primary producers are called primary consumers. According to the terrestrial ecosystem, herbivorous animals like cows, goats, humans etc. can be the primary consumers. But whenever a human consumes a herbivorous animal, he becomes a secondary consumer.
What is a Consumer in a Food Chain?
A consumer in a food chain is a living organism that eats organisms of a different population. The consumer is also called a heterotroph. Consumers are usually predatory animals such as those that eat meat, but some herbivorous consumers eat plants. For example, tigers and deer are both consumers.
What is the Primary Consumer in the Food Chain?
The organisms that eat producers are called primary consumers. Many are primary consumers and are usually small in size. The primary consumers are vegetarians or vegans. For example rabbits, grasshoppers, giraffes, herbivorous man etc.
What is a Secondary Consumer in the Food Chain?
Organisms that eat primary consumers are called secondary consumers of energy and protein. Secondary consumers can be either carnivorous or omnivorous. They can be anywhere from small animals to large predators. For example, fish, wolves etc.
What is a Tertiary Consumer in the Food Chain?
Organisms that eat primary and secondary consumers are called tertiary consumers of energy and protein. These are on top. Like tigers, lions, humans etc.
Aquatic System
What do you understand about food chains in aquatic systems?
Food Chain: It is the relationship between producers and consumers through food relationships.
For example:
Aquatic insect → small fish → big fish
Two fish and an insect are connected in a food chain.
Food webs: They are more complex and are made up of food chains. Organisms feed on and consume more than one type of organism. The food web connects:
Autotroph → Herbivore → Carnivore → Secondary carnivore
Energy and Food
Autotrophs: These are those that can make their food from inorganic sources. This process is generally accomplished through photosynthesis. Photosynthesis in aquatic systems begins with a variety of autotrophs, or producers, ranging from microscopic single-celled organisms to large aquatic plants.
FAQs
Question: What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
Answer: It reflects the linear food relationships between organisms in an ecosystem, while a food web reflects the complex network of relationships that exists between multiple interconnected food chains.
Question: What is the importance of food chains in ecosystems?
Answer: Food chains are important because they help move energy and nutrients through ecosystems from producers to consumers and ultimately to decomposers. This transfer of energy and nutrients helps sustain life in the ecosystem.
Question: How does the 10% rule apply to food chains?
Answer: The 10% rule states that only 10% of the energy available at one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level. This means that there is less energy available at each successive trophic level, so there are fewer organisms at higher trophic levels.
Question: Can the same organism be part of multiple food chains?
Answer: Yes, many organisms are part of many food chains within an ecosystem. This is because they may have multiple predators or consume multiple prey species.
Question: What is the difference between the detritus food chain and the grazing food chain
Answer: A detritus food chain starts with dead organic matter and includes decomposers and detritivores, while a grazing food chain starts with living plants and includes herbivores and carnivores.