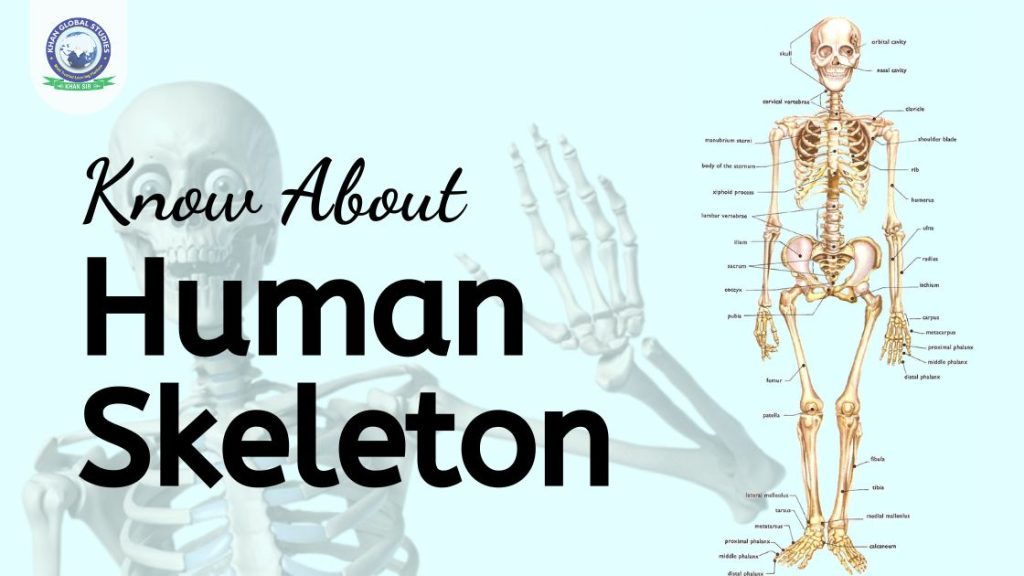
The human skeleton is a marvel of biological engineering, providing the framework that supports our bodies and protects vital organs. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of the human skeleton, its overview, functions, types and structure to gain a deeper understanding of this fundamental aspect of human anatomy.
Human Skeletal System
Apart from rocks, the structure of the skeleton also includes cartilage or bone at some places. The skeletal system is divided into two main principles-
- Axial Skeleton: This includes the oblique and elliptical axis of the body. It includes the cranium or skull, sternum and ribs, spinal cord, and hyoid bones.
- Contracted Skeleton: The skeleton consists of upper and lower rocks and their belts. There are three small bones in the middle part of each of these ears. Bones are divided into long, short, flat, cancellous and sesamoid bones.
Structure of Human Skeleton
The human skeleton is composed of various types of connective tissue, primarily bone and cartilage. Bones are made up of cells called osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts, which continuously remodel bone tissue throughout life. Each bone has a dense outer layer called cortical bone, which provides strength and stiffness, and an inner spongy or trabecular bone containing marrow and blood vessels.
Types of Human Skeletal System
According to the bones available in the human body, there are two types of skeletal system:
External skeleton: The skeleton found on the upper surface of the body is called the external skeleton, like skin in the human body, feathers in birds, and hair in animals. The function of the exoskeleton is to protect the internal organs of the body.
Endoskeleton: The skeleton found in the internal part of the body is called the endoskeleton. It forms the main structure of the body. The endoskeleton consists of two parts:
- Bone
- cartilage
Bone:- Bone is solid, hard and strong, which we generally call bones. Being made of calcium and magnesium, bones are so solid that they can bear the weight of the body. Thick and long bones are hollow from the inside, in which a fluid is found, which is called bone marrow. There are two types of bones: articular bones and cartilaginous bones. There are 206 bones in the human body in the adult stage, whereas about 300 bones are found in the newborn baby.
Cartilage:- Cartilage is formed from the connective tissues of the skeleton. It is semi-solid, flexible and transparent.
Parts of the Human Skeletal System
The human skeletal system has two parts:
- Axial Skeleton
- Appendicular Skeleton
Axial Skeleton
The axial skeleton is formed around the central axis of the body and thus includes the skull, spine, and ribs. It protects the brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs, oesophagus and major organs such as the eyes, ears, nose and tongue. The axial skeleton consists of about 80 bones, including the skull, spine, ribs, and sternum. Which is divided into three parts:
- Skull
- Spinal Cord
- Ribs
Skull
- It is divided into two parts and a total of 22 bones are found in it.
- Skull – It contains 8 bones.
- Facial bone – It consists of 14 bones.
- Apart from this, there are 3 pairs of ears.
- Apart from this, there is another one which is called Hoid.
- The ear bones are located in the middle part of the ear. The stapes bone of the ear is the smallest in our body.
Main Bones of the Skull
- Frontal
- Parietal
- Occipital
- Temporal
- Mailer
- Maxilla
- Dentary
Spinal Cord
- Its length is 70 centimetres and it has 26 bones, the total number of vertebrae is 33.
- The first vertebra is named atlas and the last one is coaxial, it is also called tail vertebra.
- There is a hole in the vertebra through which the spinal cord or spinal cord passes.
The spinal cord is divided into the following parts:-
- Neck: made up of 7 vertebrae and 7 bones
- Thorax: contains 12 vertebrae and 12 bones
- Waist: made up of 5 vertebrae and 5 bones
- Sacral: consists of 5 vertebrae and 1 bone
- Coccygeal Bone: consists of 4 vertebrae and 1 bone
Thus, there are a total of 33 vertebrae and 26 bones. There is only 1 bone in the sternum.
Ribs
Their total number is 24 or 12 pairs. They form a cage called a rib cage.
- This rib cage comprises the ribs, sternum, and thoracic vertebrae.
- Ribs 1 through 7 are called true ribs.
- The 8th, 9th and 10th pairs are called false or accessory ribs.
- The 11th and 12th pairs are called floating or movable ribs.
- Thus a total of 80 bones form the axial skeleton.
Appendicular Skeleton
The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the hands and feet. There are a total of 126 bones in it.
- Girdle – It includes the bones of the leg.
- Ensemkhala- It includes the bones of the hand.
Belts (मेखलाएं)
It connects the legs to the main axis and is also divided into two parts.
- Ansh Mekhala
- Pelvic girdle
Ansh Mekhala: It contains a total of 4 bones. It connects the front legs to the main pivot. There are two types of bones in it.
Clavicle bone: Also called the collar bone or sometimes called the beauty bone. There is one bone on both sides of it. It connects the hands to the sternum.
Scapula: It is called shoulder bone or shoulder bone. It connects the clavicle to the humerus.
Coxal bone: It is called hip bone or hip bone. There is one on both sides. Due to differences in their skeletal systems, the pelvic girdle has a pelvic arch or angle of 90 degrees in men and 100 degrees in women.
Functions of the Skeletal System
Along with strengthening the body, the skeletal system also performs many other functions, which are described below:
- The skeletal system provides strength and shape to the body.
- The exoskeleton protects the internal organs.
- It provides movement to the entire body with the help of muscles.
Functions of Bones
- Bones help the body to stand upright.
- Provides strength to the body.
- Bones give shape to the body.
- Protects other internal organs of the body.
Major joints of the Human Skeletal System
The bones of the skeletal system that join together are called joints. In common language, the joints of the elbow, knee, neck etc. are called joints. There are two types of treaties:
- Dynamic joints – The joints that provide movement to the bones are called dynamic joints, such as knee, neck, elbow, shoulder etc.
- Stable joints – These joints protect the delicate parts of the body like mouth, skull, chest etc.
What is the difference between skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle?
You have three types of muscles in your body:
- Skeletal Muscle: Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles, which means that you control how and when they move and work. The nerves of your somatic nervous system send signals to them to function. If you reach toward a book on the shelf, you are using the skeletal muscles of your neck, arm, and shoulder.
- Cardiac Muscles: Cardiac muscles are found only in your heart. They help your heart pump blood around your body. They are involuntary muscles that your autonomic nervous system controls. This means that they do things without thinking about you.
- Smooth Muscles: Smooth muscles make up your organs, blood vessels, digestive system, skin, and other areas. Smooth muscles are also involuntary. So, your autonomic nervous system controls them too. For example, the muscles in your urinary system help rid your body of waste and toxins.
Conclusion
The human skeleton is a marvel of evolution, serving as the foundation of our body’s structure, protection, and movement. From providing structural support to facilitating hematopoiesis, its functions are diverse and indispensable for our survival. Understanding the types and structure of bones helps us appreciate the complexity and efficiency of this integral aspect of human anatomy. So, let’s continue to marvel at the wonders of the human skeleton and delve deeper into the fascinating world of our skeletal system.
FAQs
Question: What is skeletal muscle?
Answer: Most of the muscles in your body are skeletal muscles. They make up between 30 and 40% of your total body mass. Tendons (tough bands of connective tissue) attach skeletal muscle tissue to bones throughout your body. Your shoulder muscles, hamstring muscles, and stomach muscles are all examples of skeletal muscles.
Question: What are the parts of the skeletal system called?
Answer: Bones.
Question- In which two parts is the skeletal system studied?
Answer: Exo and endoskeleton.
Question: Bones are made of which cells?
Answer: Mesenchyme.
Question: What causes bone growth?
Answer: Mesoderm.
Question- Which substance released from cells makes osteoblasts?
Answer: Ocean.
Question: What is the external skeleton of insects made of?
Answer: Chitin.
Question: What forms the central base of the skeleton?
Answer: Spinal Cord.
Question: What fills the space between two vertebrae?
Answer: Fibroid Pad.
Question: How long is the spinal cord in an adult human being?
Answer: 60-70 cm.
Question: How many vertebrae are there in the spinal cord?
Answer: 33.
Question: What do the concha, frontal, maxillary bone, maxillary bone and parietal bone belong to?
Answer: Skull.
Question: Nose, skull bones, lacrimal bones, bower, palatine, maxillary, mandible, spongy bones are related to?
Answer: Face.
Question: What are the spinal cord, chest bone and ribs related to?
Answer: Torso.
Question: How many bones are ribs made of?
Answer: 24.
Question: What phalanges, humerus, radius, ulna, carpus, and metacarpals are the bones of?
Answer: Hand.
Question: Whose bones are the Patella, Tarsus, Metatarsus, Femur, and Tibio Fibula?
Answer: Feet.
Question: What is the number of bones in the brain chamber of our body?
Answer: 8.
Question: What is the number of sternum?
Answer: 8.
Question: How many bones are there in the human face?
Answer: 14.