Cell division occurs when an original cell divides into two or more cells called daughter cells. It typically occurs as part of a larger cell cycle. All cells reproduce by dividing into two, where each parent cell gives rise to two daughter cells.
These newly formed daughter cells can divide and grow, creating a new cell population composed of the division and growth of a single parental cell and its descendants.
In other words, such cycles of growth and division allow a cell to form a structure consisting of millions of cells.
Types of Cell Division
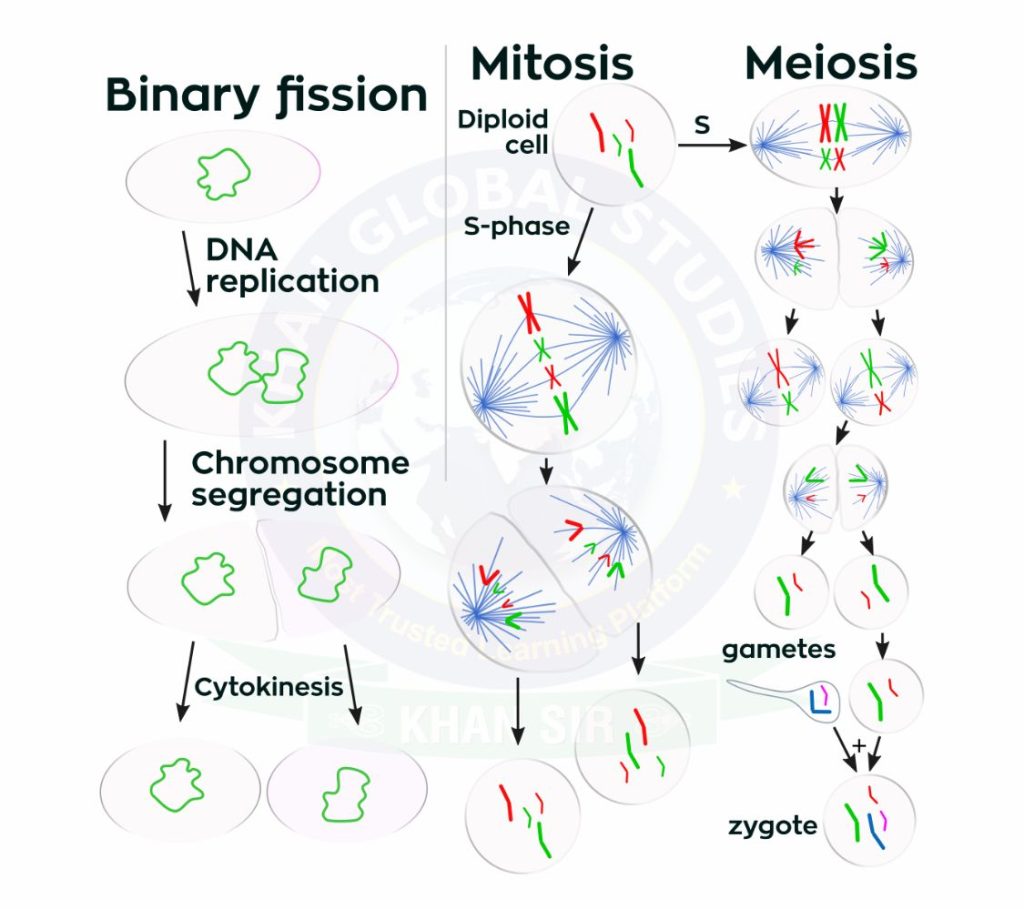
There are two types of cell division, the first of which is somatic division, in which each daughter cell copies the parent cell in mitosis. The other is meiosis, which divides into four haploid daughter cells.
- Mitosis: The process cells use to make exact copies of themselves. Mitosis is seen in almost all body cells, including eyes, skin, hair, and muscle cells.
- Meiosis: In this type of cell division, sperm or egg cells are produced rather than identical daughter cells as in mitosis.
- Binary Fission: Single-celled organisms such as bacteria replicate themselves to reproduce.
Phases of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle has two primary phases:
- Interphase: This phase was thought to represent the resting phase between subsequent cell divisions, but new research has shown that it is a very active phase.
- M phase (mitosis phase): This is where actual cell division takes place. There are two major steps in this phase, cytokinesis and karyokinesis.
The interface further involves three steps:
- G0 phase (resting phase): The cell neither divides nor prepares itself for division.
- G1 phase (Gap 1): The cell is metabolically active and continues to grow during this phase.
- S phase (synthesis): DNA replication or synthesis occurs during this phase.
- G2 phase (Gap 2): Protein synthesis occurs in this phase.
- Quiescent state (G0): Cells that do not undergo further division exit the G1 phase and enter the quiescent state. This phase is known as the inactive phase (G0) of the cell cycle.
M phase consists of four stages, namely:
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase



