The Sun is a 4.5 billion-year-old star located in the center of our solar system, with bright gases inside. The gravity of the Sun is responsible for keeping everything from the largest planets to small debris in its classrooms. It’s a source of energy and light for our planet Earth.
Sun activity It is a powerful explosion or steady stream of charged particles that send it affects our solar system and in the last decade in the last decade, the activity of the Sun’s activity cycle or the sun cycle such as the phenomenon of it, such as solar flares, changes, changes, in changes Sun’s magnetic field, etc.
The Important Point of the Sun
- The Sun was born 4.5 billion years ago.
- It is made of hydrogen and helium gas.
- Nuclear fusion occurs in the sun, causing light and heat in it.
- The Sun’s intention is 150 million km (15 million km) away from the Earth.
- It takes 8 minutes 20 seconds to get sunlight from the Sun to Earth.
- The diameter of the Sun is 1.4 million km. It is a medium-sized star.
- The surface temperature of the Sun is 5,500 ° C.
- It revolves like the earth. Meaning, the sun takes 27 days of the Earth for a day.
- The nearest star of the Sun is Alpha Centauri. It is a group of three stars called the Triple Star System.
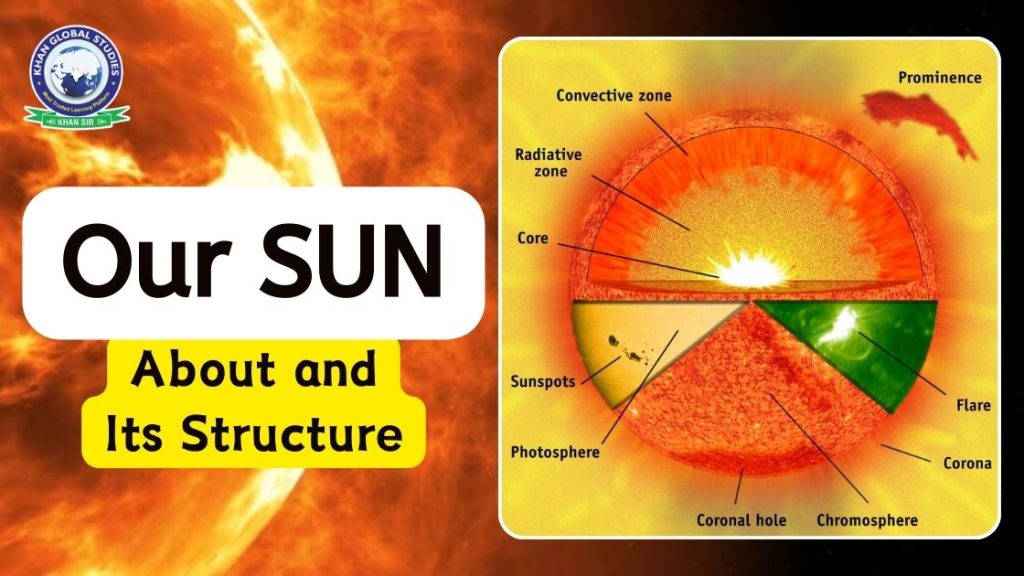
Structure of the Sun
The sun is a whole gas ball. There is no solid substance in it. It is only made of separate gas. It has the most hydrogen and helium gas. The gas in it is hydrogen (23.46%), helium (24.85%), oxygen (0.77%), carbon (0.29%), iron (0.16%), neon (0.12%), nitrogen (0.09%), silicon ( 0.07%), magnesium (0.05%), sulfur (0.04%).
Two parts participate in the structure of the Sun, one is the inner surface and the other is the surface and region above the solar atmosphere. These two parts are made of different layers. Therefore, we give all layers and give complete information about it.
Internal part
- Core
- Radiation Area
- Tachocline
- Convection Zone
Solar environment:-
- Photosphere
- Chromosphere
- Corona
Internal Part of the Sun
Core
- The inside of the Sun is called the core.
- The core extends 140,000 – 170,000 kilometers inside the Sun.
- It is the hottest part of the Sun. Its temperature is 15 million°C.
- Its density is 150 g/cm 3.
- It consists of nuclear fusion. Here, hydrogen autumn and other hydrogen autumn reactions form helium and a lot of energy is born.
- Photon is born there due to nuclear fusion. Photon is a type of electromagnetic radiation that contains infrared, visible and ultraviolet light.
- Photos in this layer are very powerful.
- This includes cases in the plasma state. The plasma is the 4th state of the substance.
Radiation Area
- This layer comes after the core.
- This layer is filled with charged particles.
- In this layer, the photo comes from the core gives their energy.
- It is the most pearl in the Sun.
- It takes 1 lakh 70 thousand years to make pictures made in light or sun core on this layer.
- Touchline
- This layer is between the radiation area and the convection area.
- It is a very thin layer.
- In this layer, the magnetic field of the Sun is produced.
Convection Zone
- It tops the surface of the sun.
- This radioactive area is the above layer of the connective area.
- The density of plasma in this layer is very low. The density of this layer is 0.2 g/m3.
- The thickness of this layer is 1.39 km.
- This layer contains 6 million degrees Celsius temperatures on the inner side and 6000 degrees Celsius on the outside.
- This layer of the Sun is very upheaval and there is a lot of sound in this layer.
- It keeps some of its electrons for heavy ions (such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, calcium and iron). This material makes it more opaque, making it difficult to move radiation through it.
- This layer absorbs harmful gamma rays and weakens the photographs.
Solar Environment of the Sun
Photosphere
- It is a beautiful part of the Sun.
- This is the lowest level in the Sun’s atmosphere.
- It is 100 km thick.
- Snapsports appear in it.
- This layer is covered at the time of solar eclipse.
- With this layer, the pictures of Sun appear in the spectrum light copy.
Chromosphere
- The chromosphere is the second layer of the solar environment that occurs above the photo.
- The temperature of this layer is 6000°C to 20000°C.
- This layer is seen at the time of solar eclipse.
- In this layer, H alpha radiation filters the photographs, and visible light emerges from this layer.
Corona
- It is the outstanding layer in the Sun.
- This layer is fully visible at the time of solar eclipse.
- This layer brings very bright light.
- Astronomers say they have found “coronium” in this layer.
- Due to the “coronium” gas, the temperature of this layer exceeds 1,000,000°C.
- This layer contains a lot of dust and free electrons, so it breaks the photo.
How does sunlight reach the Earth?
The Rays/Photons of the sun arise due to atomic fusion at the root of it. It then goes out of the photo and enters the radiation area. The radiation area is very dense, from this layer the sun waves from one particle to another particle and very energy loss. After that, after 100000 years, the photon exits this radiation area and enters the convection field. The interior of the convection area is very hot and is very cold towards spring. Therefore, by identifying here, the photo comes on the zone and then goes down and goes down. Similarly, due to long-running, the photo gives too much energy to them and the photo comes from this layer to the surface.
The photo then enters the photon in the first layer of the solar view. From there, the temperature of the photographs begins to grow again, after which it is chromosomal and recognised in the corona. Asanis is not able to exit due to the magnetic field in Corona. Therefore, on this layer where the magnetic energy is low, it turns out to be the bubble’s shape and turns to the earth. It takes 1000000 years and 1700000 years to come from the origin of the Sun to Corona.
Then it takes 8 minutes 30 seconds to identify Sun Ray from Corona to Earth. Then after identifying with the Earth, the loss of sun rays in the very lover of the Earth becomes a factor filter, and then we see visible light.
We need 21 tons of coal to make energy from the sun in 1 hour. According to estimates, 5000 trillion units of energy in India meet the Sun, which is very high according to our needs.
We do very little using sunlight. Such as summer water, dried clothes, etc. This power of the sun is called Solar Thermal Energy.
FAQs
Question: How big is the Earth of the Sun?
Answer: It has increased by 109 times the Earth.
Question: What is the distance from the Sun to Earth?
Answer: 14 million 96 lakh km or about 15 million km away.
Question: How old is the sun?
Answer: 4.6 billion years.
Question: How long does it take to come to Earth with sunlight?
Answer: Hydrogen and helium are high in the sun.
Question: What is the surface temperature of the Sun?
Answer: 5500 ° C.
Question: Which process is the main source of sun energy?
Answer: Hydrogen change in Helium (Nuclear Fusion).
Question: What is the color of the sun?
Answer: When every color of light is added, your color eventually turns white. Thus, the sun appears yellow on the Earth and white in space. On Earth, the atmosphere also plays a role in the color of the Sun.